Introduction#
Timflow transient is a submodule for the modeling of transient multi-layer groundwater flow with analytic elements.
The head, flow, and leakage between aquifer layers may be computed analytically at any point in the aquifer system and at any time.
Tutorials and how-to guides for getting started with timflow transient.
Timflow transient basic concepts and elements explained.
Timflow transient example notebooks.
Transient cross-section models.
Pumping test benchmark notebooks.
Comparing timflow transient to known solutions.
Quick Example#
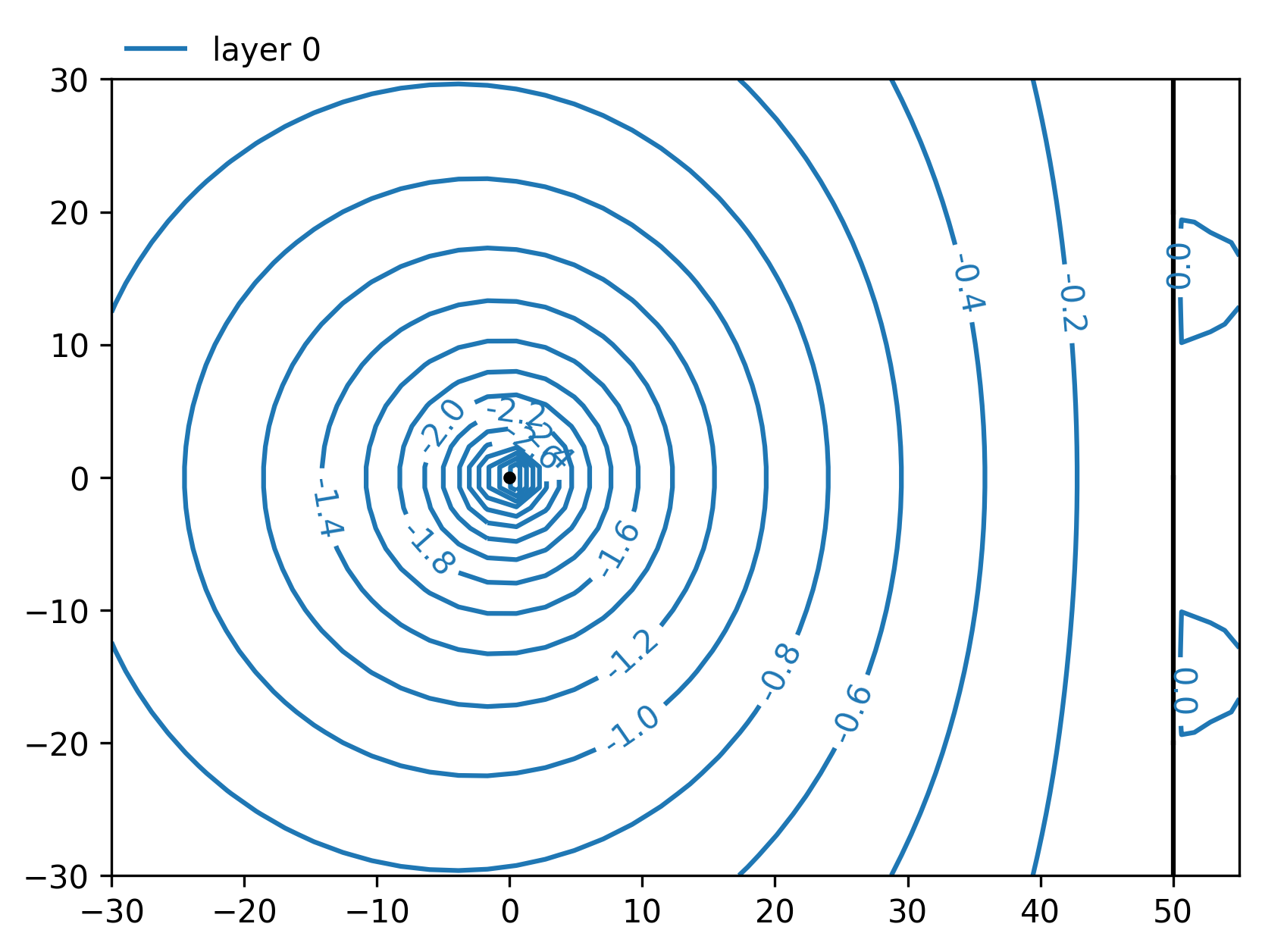
In this example a well is modelled near a river in a single aquifer.
# Import python packages
import numpy as np
import timflow.transient as tft
# Create model
ml = tft.ModelMaq(
kaq=10, z=[20, 0], Saq=[0.1], phreatictop=True, tmin=1e-3, tmax=100
)
# Add a river with a fixed water level
yls = np.arange(-100.0, 101, 20)
xls = 50.0 * np.ones_like(yls)
river = tft.RiverString(ml, xy=list(zip(xls, yls)), tsandh='fixed')
# Add a well
well = tft.Well(ml, 0.0, 0.0, rw=0.3, tsandQ=[(0, 1000)])
# Solve model
ml.solve()
# Plot head contours at t=2 days
ml.plots.contour(win=[-30, 55, -30, 30], ngr=40, t=2, labels=True, decimals=1)
In this example a well is modelled near a river in a single aquifer.
Approximations#
The Dupuit approximation is applied to aquifer layers, while flow in leaky layers is approximated as vertical.
